44 if we denote speed by s, distance by d and time by t, the relationship between these quantities is
[email protected] - pocketopera.it 09.03.2022 · Sep 27, 2016 · 14. These days we try to not go more than 5-6 hrs between stops. Average speed is calculated by dividing an object's distance traveled by the time elapsed during travel. Times decimal of hour by 60 to get minutes: 1. Divide both sides by 15. Calculate the average speed for each journey, using the Define average speed. Therefore, distance … If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the ... Speed is given bySpeed=dfrac{distance(D)}{time(T)}S=dfrac{D}{T} | Snapsolve If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the relation between these quantities is ( )A. S=Dtimes TB. T=dfrac{S}{D}C. S=dfrac{1}{T}cdot DD.
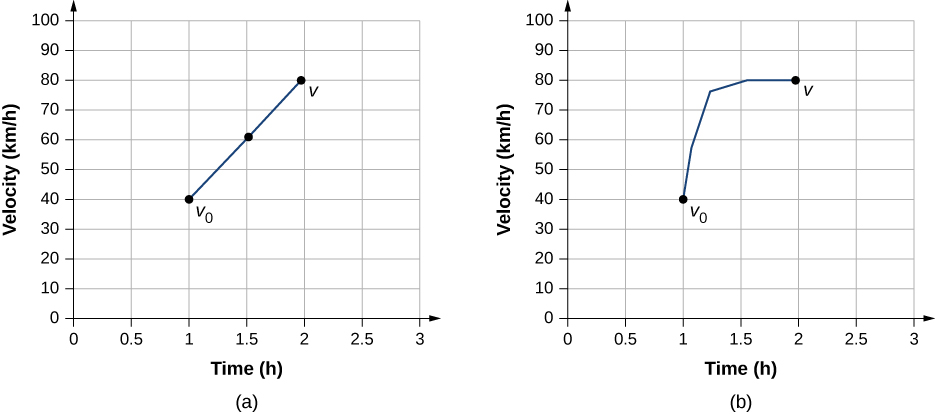
3.4 Motion with Constant Acceleration - University Physics ... We are asked to solve for time t. As before, we identify the known quantities to choose a convenient physical relationship (that is, an equation with one unknown, t.) Figure 3.24 Sketch of a car accelerating on a freeway ramp. Solution Again, we identify the knowns and what we want to solve for. We know that x 0 = 0, x 0 = 0, v 0 = 10 m/s, a = 2.00 m/ s 2 v 0 = 10 m/s, a = 2.00 …
If we denote speed by s, distance by d and time by t, the relationship between these quantities is
Spacetime - Wikipedia Although measurements of distance and time between events differ for measurements made in different reference frames, ... In S′ these events are only separated in time, they happen at the same place in S′. Because of the invariance of the spacetime interval spanned by these two events, and the nonzero spatial separation d in S, the temporal distance in S′ must be smaller … 3.4 Motion with Constant Acceleration – University Physics ... We then simplify the equation. The units of meters cancel because they are in each term. We can get the units of seconds to cancel by taking t = t s, where t is the magnitude of time and s is the unit. Doing so leaves . We then use the quadratic formula to solve for t, which yields two solutions: t = 10.0 and t = −20.0. A negative value for ... Particle in a Box : Absorption Spectrum of Conjugated Dyes Since ∆E = hν = hc/λ, where c is the speed of light and λ is the wavelength, we have: (3) λ= + 8 1 ma2 hc N() The polymethine chain stretches from the one nitrogen atom to the other nitrogen atom. Let us denote the number of double bonds within in the chain by j; then N = (2j + 2). In our example dye, j = 5, therefore N = 12; count the π electrons to check. Huhn assumed the length …
If we denote speed by s, distance by d and time by t, the relationship between these quantities is. If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the ... If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these Quantities is A) S=D*T B) T=S/D C) S=1/T*D D) S=T/D - 20117682 praiseye praiseye 28.07.2020 Physics Primary School answered If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the ... If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is . If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is . Books. Physics. NCERT DC Pandey Sunil Batra HC Verma Pradeep Errorless. Chemistry. NCERT P Bahadur IIT-JEE ... Measurements of AC Magnitude | Basic AC Theory ... The problem of trying to describe the changing quantities of AC voltage or current in a single, aggregate measurement is also present in this saw analogy: how might we express the speed of a jigsaw blade? A bandsaw blade moves with a constant speed, similar to the way DC voltage pushes or DC current moves with a constant magnitude. A jigsaw blade, on the other hand, … If we denote speed by S , distance by D and time by T the ... Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ If we denote speed by S , distance by D and time by T the relationship these equation is? Solve Study Textbooks Guides. Join / Login >> Class 11 >> Physics >> Motion in a Straight Line >> Speed and Velocity >> If we denote speed by S , distance by D .
Chapter 20 Rigid Body: Translation and Rotational Motion ... In order to understand the relationship between . V. cm. and ω. cm , we consider the displacement of the center of mass for a small time interval Δ. t (Figure 20.5). Figure 20.5 . Displacement of center of mass in ground reference frame. From Eq. (20.2.3) the . x-component of the displacement of the center of mass is . Δ. X. cm = V. cm. Δ ... If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the ... Answer:the answer is option c) 1/T*D damayantikisan09 damayantikisan09 01.12.2020 Science Secondary School answered If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is (a) S = D × T (b) T = S / D (c) S = 1 / T * D EOF Annual Average Daily Traffic - an overview - ScienceDirect 15.01.2013 · where S=Speed in mph or fps; d=distance traversed in miles or ft; t=time to traverse the distance d. The average or mean speed can be computed in two different ways. Mathematically, the time mean speed is an average of the individual vehicle speeds and the Space mean speed is the HM of the individual speeds. Annual Average Daily Traffic (AADT): …
If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the ... If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is ... Unanswered; Ask a Question; Learn; Ask a Question. If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is ... asked Jan 23, 2018 in Science by Rohit Singh (65.1k points) If we denote speed by S ... Question 5 If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time ... Question 5 If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities isa S=D Tb T = S / Dc S =1/ T × Dd S=1/D Motion and Time Class 7 Extra Questions ... - Learn CBSE 07.06.2019 · If we denote speed by S, distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these Quantities is [NCERT Exemplar] Answer: (d) \(S=\frac{1}{T} \times D\) Question 6. Which one records the distance travelled by a vehicle? (a) Speedometer (b) Manometer (c) Motometer (d) Odometer Answer: (d) Odometer. Question 7. The correct symbol to represent the speed … NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Science Chapter 13 Motion and Time ... 20.04.2019 · If we denote speed by 5, distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is (a) S=D × T (b) T=S/D (c) S=1/T x D (d) S=T/D Solution: (c) Question 6. Observe figure. The time period of a simple pendulum is the time taken by it to travel from (a) A to B and back to A. (b) OtoA, 4 to 6 and 8 to 4. (c) B to A, A to B and B to O. (d) A to B. …
If we denote speed by S, the distance by D and time by T ... If we denote speed by S, the distance by D and time by T, the relationship between these quantities is (a) S = D × T (b) T = S/D (c) S = 1/TxD (c) S = T/D - Get the answer to this question and access a vast question bank that is tailored for students.
Particle in a Box : Absorption Spectrum of Conjugated Dyes Since ∆E = hν = hc/λ, where c is the speed of light and λ is the wavelength, we have: (3) λ= + 8 1 ma2 hc N() The polymethine chain stretches from the one nitrogen atom to the other nitrogen atom. Let us denote the number of double bonds within in the chain by j; then N = (2j + 2). In our example dye, j = 5, therefore N = 12; count the π electrons to check. Huhn assumed the length …
3.4 Motion with Constant Acceleration – University Physics ... We then simplify the equation. The units of meters cancel because they are in each term. We can get the units of seconds to cancel by taking t = t s, where t is the magnitude of time and s is the unit. Doing so leaves . We then use the quadratic formula to solve for t, which yields two solutions: t = 10.0 and t = −20.0. A negative value for ...
Spacetime - Wikipedia Although measurements of distance and time between events differ for measurements made in different reference frames, ... In S′ these events are only separated in time, they happen at the same place in S′. Because of the invariance of the spacetime interval spanned by these two events, and the nonzero spatial separation d in S, the temporal distance in S′ must be smaller …

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-533596181-1--57a0e6103df78c3276e56e07.jpg)




























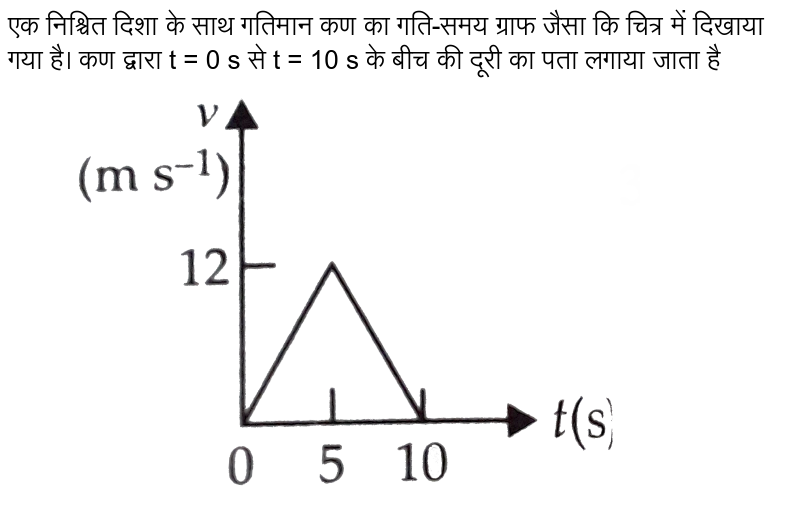


0 Response to "44 if we denote speed by s, distance by d and time by t, the relationship between these quantities is"
Post a Comment